Protocol Analysis
LeCroy&squot;s solution for FireWire testing is the FireInspector Plus system. This all-in-one test platform offers traffic generation with integrated protocol analysis. The traffic generator includes a graphical interface which makes it easy to construct, send and receive 1394 isochronous, asynchronous and PHY packets to test functionality, compatibility and error recovery.
FireInspector provides everything needed for detailed IEEE-1394 Protocol analysis including real-time hardware triggering and filtering on the critical components of FireWire traffic. LeCroy&squot;s Expert Analysis software simplifies the overall debug process by using collapsible, color-coded packets to show higher level 1394 protocol transactions in a format that is easy to understand.
Learn more about IEEE 1394 Technology
IEEE 1394 Overview
IEEE 1394 is a versatile, high-speed serial interface, designed to connect consumer electronics devices and personal computers. Apple and Texas Instruments developed and branded this technology "FireWire" in the mid-1990s as a low cost, high speed interface for attaching peripherals to Macintosh computers. Low or no cost licensing agreements to silicon and PC vendors as well as consumer electronics manufacturer抯 have significantly increased the use of 1394 in the electronics industry. Nearly all of the big-name PC manufacturers now offer models with a 1394 connection. As convergence of computing and digital media continues, 1394 FireWire is uniquely positioned to bridge the digital entertainment systems of tomorrow.
Features
IEEE 1394 was designed with a rich set of features primarily targeted at the PC and consumer electronic market segment. It provides a peer-to-peer network based topology that supports isochronous transfers making 1394 ideal for connecting electronic devices with real time processing requirements. This has solidified 1394&squot;s position as the primary interconnect for transferring digital video to PCs.
1394 devices on the market today conform to either the original IEEE 1394-1995 specification or its backward-compatible supplement, IEEE 1394a-2000. The 1394 standards group has pioneered efforts to further evolve FireWire as the primary interface for networking multimedia devices within the home and automotive environments.
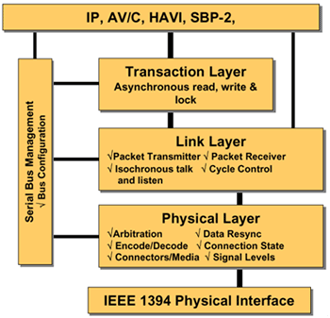
IEEE-1394-1995 - The original specification for 1394 includes the following capabilities:
- Isochronous and asynchronous data transfers which allow for support of streaming of real time AV data as well as command functions, control operations, and bulk data transfers, respectively.
- Guaranteed bandwidth for real time applications means that channels are secured for long transmissions, and a fair bus access scheme ensures asynchronous data gets its turn on the bus.
- Peer to peer communications means that no central node/server is defined in the network and that each 1394 node in the network can support itself as well as maintain the network.
- Plug and play translates into ease of use for the consumer, and is enabled by the features mentioned above.
- Small, low cost standard cables and connectors that can be used across all market sectors.
- Up to 63 nodes can be connected per bus for extensive 1394 networks.
1394A - The most widely used version of FireWire is 1394a. This is a supplement to the original - 1394-1995 specification and includes the following improvements:
- Arbitration accelerations improves efficiency of the bus.
- Reset improvements reduces the disruption caused when nodes are added and removed from the bus.
- Support for fine-grained power management which is particularly useful in portable computing applications
- Specification of a 4-pin connector
- Improved in the PHY-Link interface
Architecture
 The topology of a 1394 network resembles a tree structure. Each node on a 1394 network functions as a repeater, forwarding signals to the next node in a daisy chained. A FireWire network can contains up to 64 Nodes per Bus with Bridges Linking Buses together to allow up to 64,000 nodes. A 1394 network can be set up by connecting equipment with the appropriate cables, with no need for address set-up. Devices can be operated continuously without interference even if new equipment is added to the 1394 network.
The topology of a 1394 network resembles a tree structure. Each node on a 1394 network functions as a repeater, forwarding signals to the next node in a daisy chained. A FireWire network can contains up to 64 Nodes per Bus with Bridges Linking Buses together to allow up to 64,000 nodes. A 1394 network can be set up by connecting equipment with the appropriate cables, with no need for address set-up. Devices can be operated continuously without interference even if new equipment is added to the 1394 network.
AV/C - AV/C is a massive specification that encompasses dozens of subordinate specs and provides a universal way to describe the commands and data structures for consumer and professional electronic audio/video devices. This includes the transport of IEC 60958 digital format, raw audio samples, and MIDI data. It includes Common Isochronous Packets (CIP) module that defines the structure of the isochronous packets used within this standard.
Digital Transmission Content Protection (DTCP) - also known as "5C", this copyright protection protocol was created when Intel, Hitachi, Sony, Matsushita, and Toshiba joined their various proposals together in a legal/technical structure to meet the needs of both consumer electronics and the PC industry. The technology uses FireWire as a transport and combines encryption and key management in a comprehensive platform for protecting digital content rights.
Direct Printing Protocol (DPP) - direct printing protocol (DPP) provides a symmetric, peer-to-peer data transport between imaging devices, such as cameras, and 1394 equipped printers. Devices that implement DPP allow printing to take place without involving a host PC.
Home Audio Video interoperability (HAVi) - HAVi standard is a set of APIs and associated protocols for interoperability and interactivity for 1394 peripherals.
Serial Bus Protocol - SBP defines standard ways of encapsulating device commands over 1394 and is essential for Hard Drives, printers, scanners, and other devices. SBP provides a scalable DMA model for command processing and queuing IO operations to the peripheral while placing minimal load on the CPU.
IP/1394 - The IP/1394 specification details how to carry Internet protocol (IP) streams on 1394 busses. It currently specifies IPv4 and configuring DHCP over 1394 so that devices can dynamically acquire IP addresses.
IDB-1394 (Automotive) - A high-speed network for transporting digital audio/video, IDB-1394 includes an automotive-specific message set. Based on AV/C protocol, it brings interoperability with consumer devices that use IEEE 1394. The IDB spec is also targeted at automotive instrumentation such as onboard diagnostics and defines a more appropriate physical layer for the demands of automotive applications.
Efforts are underway to simplify the vast number of protocols that are part of 1394 by organizing these systems into device classes. For example, all the various camcorders and VCRs are being combined into a "tape recorder" class along with possible future audio recorders, and the various mass storage devices such as CDs, DVDs, MDs, and hard disks have been combined into a "disk" class.
